A Guide For Six Sigma DMAIC
In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations constantly strive to enhance efficiency, minimize defects, and optimize processes to meet customer demands. In pursuit of operational excellence, many turn to methodologies like Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) as a systematic approach to achieve sustainable improvements. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s and popularized by companies like General Electric, Six Sigma DMAIC has become a cornerstone in the realm of process improvement.
Who developed Six Sigma DMAIC and when?
Six Sigma DMAIC was developed by Motorola in the 1980s. It gained widespread recognition and adoption when General Electric successfully implemented it in the 1990s.
Defining Six Sigma DMAIC:
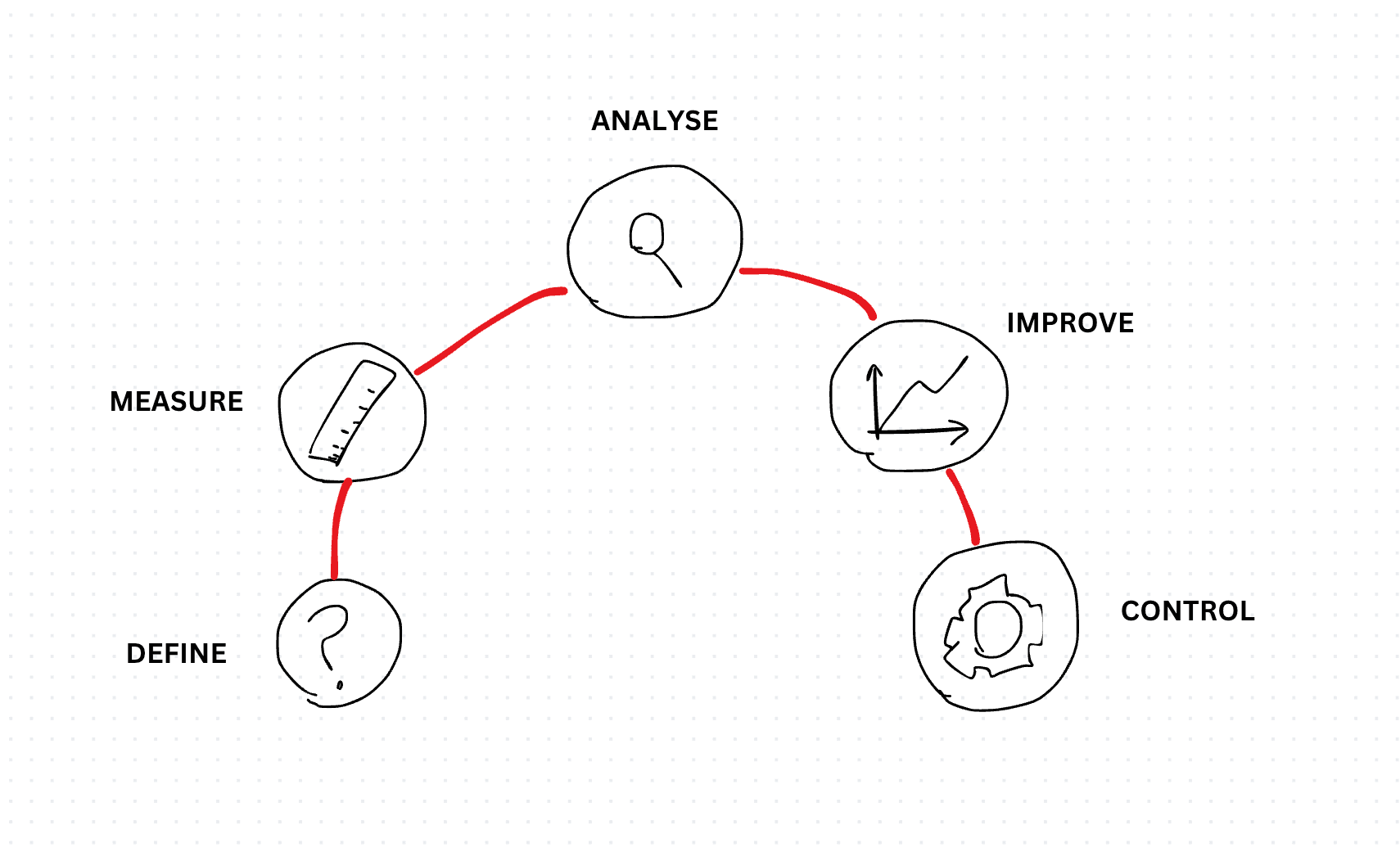
Six Sigma DMAIC is a structured, data-driven methodology aimed at improving processes by eliminating defects and reducing variations. The acronym DMAIC outlines the five phases of this methodology:
- Define: This phase involves identifying the project goals, scope, stakeholders, and deliverables. It's crucial to have a clear understanding of the problem at hand, the process to be improved, and the expected outcomes.
- Measure: In this phase, relevant data is collected to establish the current performance of the process. Key metrics are identified, and data is analyzed to quantify the extent of the problem and establish a baseline for improvement.
- Analyze: The analyze phase delves deeper into the root causes of the issues identified in the measure phase. Various tools and techniques such as root cause analysis, fishbone diagrams, and statistical analysis are employed to uncover underlying factors contributing to defects or variations.
- Improve: Based on the insights gained from the analysis phase, potential solutions are developed and implemented to address the root causes of the problem. These solutions are aimed at optimizing the process and reducing defects while considering factors like cost-effectiveness and feasibility.
- Control: The final phase focuses on ensuring that the improvements made are sustained over time. Control mechanisms are put in place to monitor the process and its performance, enabling quick identification and correction of deviations from the desired standards.
Why Six Sigma DMAIC?
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Six Sigma DMAIC relies heavily on data and statistical analysis to drive decision-making. By leveraging data, organizations can make informed choices and prioritize improvement efforts based on objective evidence.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Understanding and meeting customer requirements lie at the core of Six Sigma DMAIC. By aligning process improvements with customer needs and expectations, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Continuous Improvement: Six Sigma DMAIC promotes a culture of continuous improvement wherein processes are constantly monitored, analyzed, and refined to achieve ever-higher levels of performance. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing learning and adaptation to changing circumstances.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Successful implementation of Six Sigma DMAIC often requires collaboration across different functions and departments within an organization. By fostering collaboration, organizations can harness the collective expertise and perspectives of diverse teams to drive meaningful change.
How can organizations get started with implementing Six Sigma DMAIC?
Organizations can start by training key personnel in Six Sigma methodologies and tools. They can then identify projects aligned with organizational goals and apply the DMAIC framework to drive process improvement initiatives. Continuous training, measurement, and feedback are essential for sustaining improvements over time.
Conclusion:
Six Sigma DMAIC stands as a powerful methodology for organizations seeking to achieve operational excellence and drive continuous improvement. By following its structured approach, organizations can systematically identify, analyze, and address process inefficiencies, leading to enhanced quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. As businesses navigate an increasingly complex and competitive landscape, Six Sigma DMAIC provides a proven framework for driving meaningful and sustainable change.